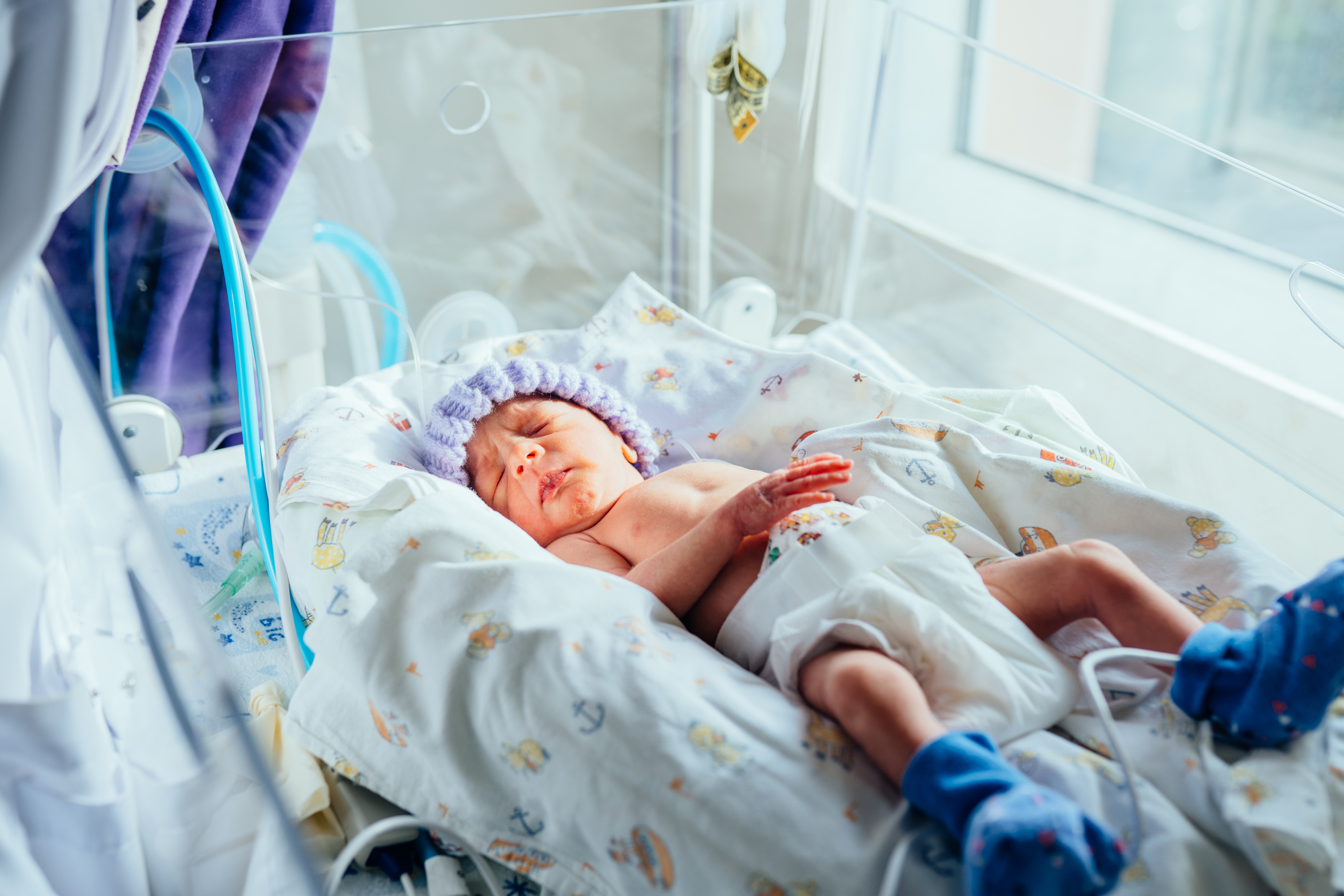
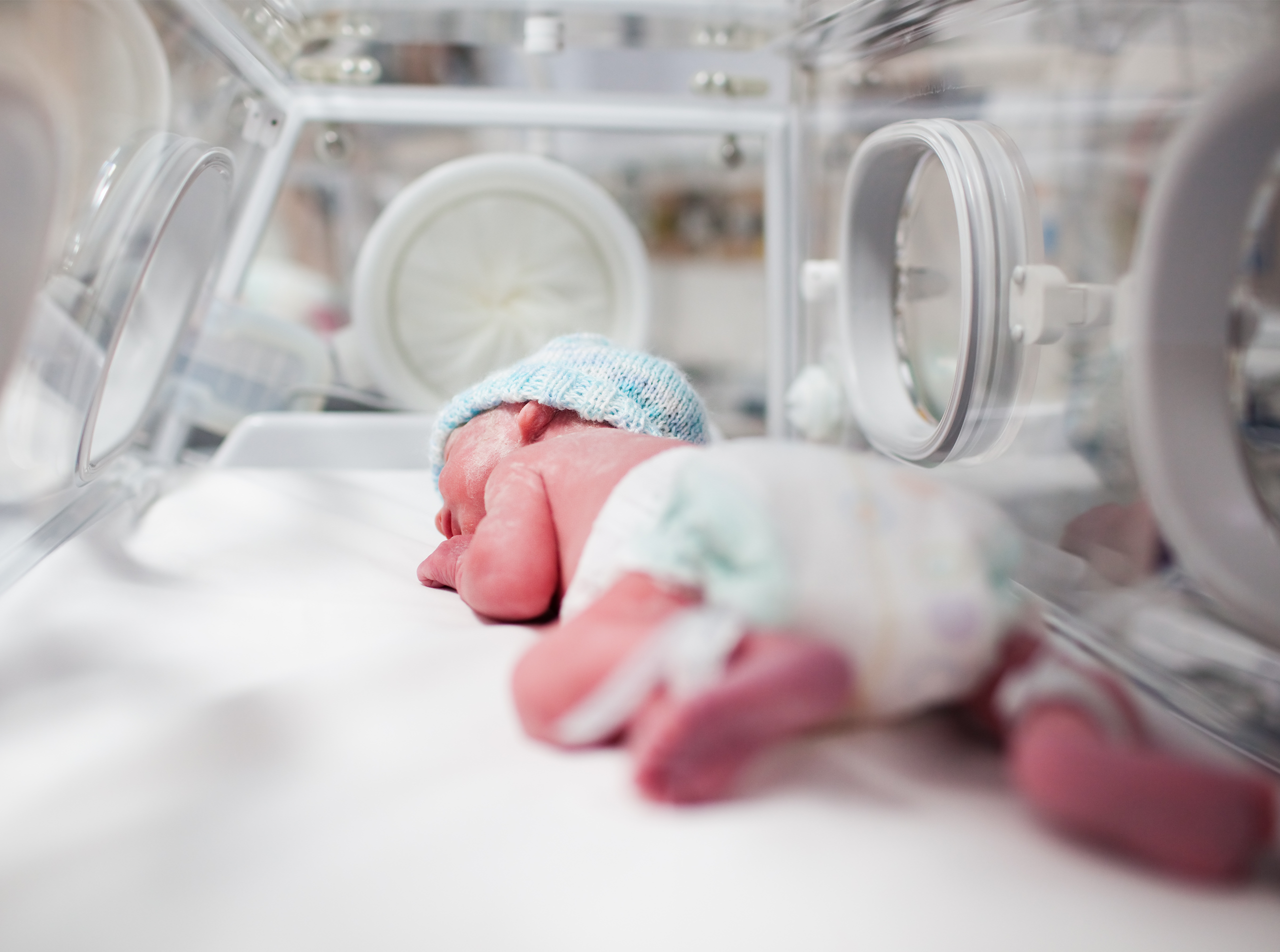
TRANSCUTANEOUS MONITORING (TCM)
Optimize ventilation while reducing blood draws
Continuous, accurate CO2 values that help titrate ventilation and deliver less invasive care through blood draw reduction.
ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY (EIT)
Assess regional lung function at the bedside
Real-time regional lung function images inform ventilation strategies to help clinicians personalize care and achieve optimal outcomes.


Cluster care

Preserve skin integrity


CO2 monitoring can help clinicians determine effective ventilatory support

Characterize regional lung function

Deliver personalized respiratory support

Cluster care

Preserve skin integrity

Deliver gentle, effective ventilation

Characterize regional lung function
Deliver personalized respiratory support

Deliver gentle, effective ventilation
Benefits for Patients
Benefits for Providers
Benefits for Facilities
The Drawbacks of Blood Draws: Transcutaneous Technology Can Help
The implementation of transcutaneous monitoring in one NICU was associated with a 25% decrease in blood draws on ventilated patients.1 Learn more below about why reducing blood draws is an important initiative in neonatology.
- Mukhopadhyay S, Maurer R, Puopolo KM. Neonatal Transcutaneous Carbon Dioxide Monitoring–Effect on Clinical Management and Outcomes. Respir Care. 2016;61(1):90-97. doi:10.4187/respcare.04212
Explore TCM Products & Support
Learn more about transcutaneous monitoring technology or view our product resource library to support an existing system.
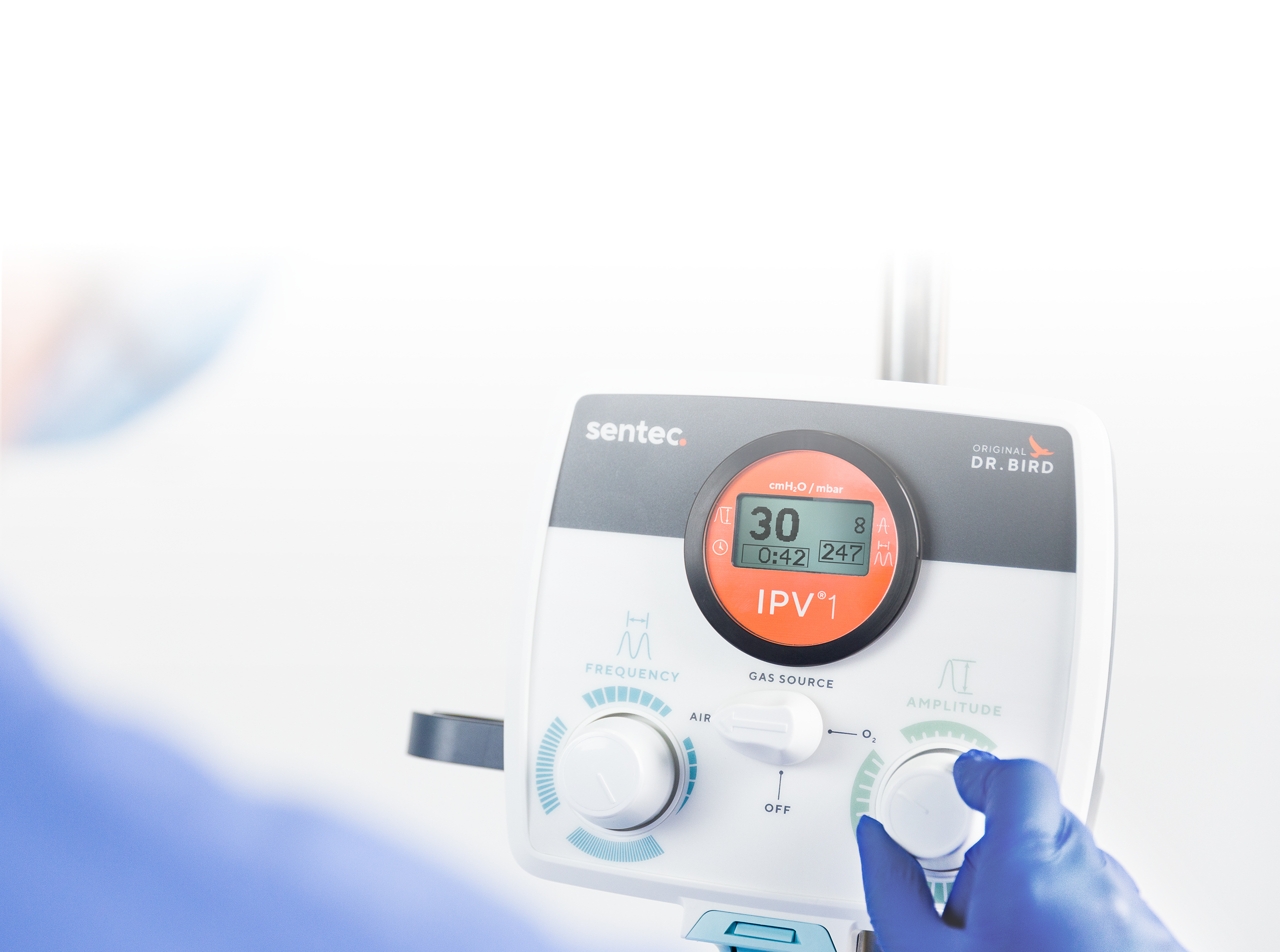
IPV THERAPY IN NEONATAL AND PEDIATRIC CARE
Airway clearance therapy for the delicate lungs of neonates and children
Sentec IPV Therapy is an effective, safe, and well-tolerated airway clearance therapy that restores gas exchange capacity for diverse respiratory patients. Adjustable settings place control in caregivers’ hands, enabling safe, customized therapy for patients in the NICU and PICU.
IPV THERAPY
IN NEONATAL AND PEDIATRIC CARE
Airway clearance therapy for the delicate lungs of neonates and children
Sentec IPV Therapy is an effective, safe, and well-tolerated airway clearance therapy that restores gas exchange capacity for diverse respiratory patients. Adjustable settings place control in caregivers’ hands, enabling safe, customized therapy for patients in the NICU and PICU.
Benefits for Patients
Benefits for Providers
Benefits for Facilities
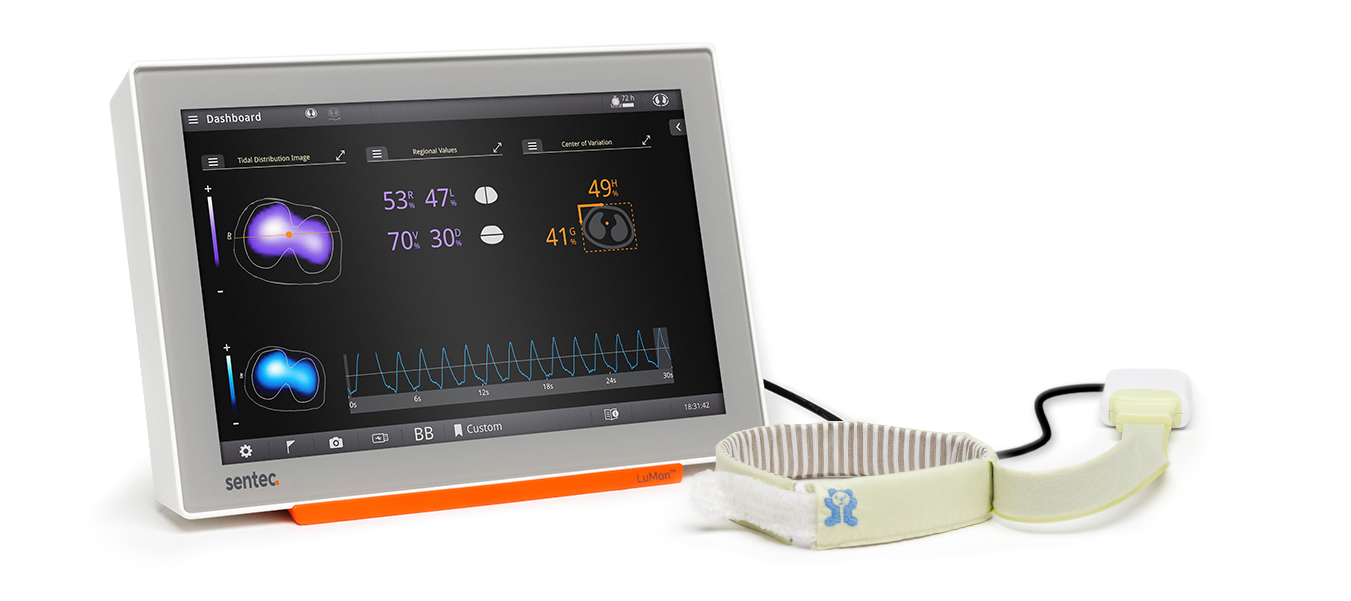
EIT IN THE NICU
Real-time regional lung function monitoring at the bedside
The LuMon™ System enables clinicians to assess regional lung function in neonates and infants continuously at the bedside without radiation exposure.
Availability of the LuMon™ System is dependent on country and product version. The LuMon™ System is currently available for investigational use only in the United States. Request information below to be notified of availability in your area.
EIT IN THE NICU
Real-time regional lung function monitoring at the bedside
The LuMon™ System enables clinicians to assess regional lung function in neonates and infants continuously at the bedside without radiation exposure.
Availability of the LuMon™ System is dependent on country and product version. The LuMon™ System is currently available for investigational use only in the United States. Request information below to be notified of availability in your area.
Benefits for Patients
Benefits for Providers
Benefits for Facilities

The LuMon™ Belts, Sentec’s textile EIT belts for neonates/infants, were clinically validated in a multi-center study on 200 neonates and infants (mean gestational age of 31±5 weeks; range: 24-42 weeks) within the European Union Horizon 2020 CRADL project, of which Sentec was part.
Explore EIT Products & Support
Learn more about electrical impedance tomography or view our product resource library to support an existing system.

The LuMon™ Belts, Sentec’s textile EIT belts for neonates/infants, were clinically validated in a multi-center study on 200 neonates and infants (mean gestational age of 31±5 weeks; range: 24-42 weeks) within the European Union Horizon 2020 CRADL project, of which Sentec was part.
Explore EIT Products & Support
Learn more about electrical impedance tomography or view our product resource library to support an existing system.

The LuMon™ Belts, Sentec’s textile EIT belts for neonates/infants, were clinically validated in a multi-center study on 200 neonates and infants (mean gestational age of 31±5 weeks; range: 24-42 weeks) within the European Union Horizon 2020 CRADL project, of which Sentec was part.
Explore EIT Products & Support
Learn more about electrical impedance tomography or view our product resource library to support an existing system.






